Serial Vs Parallel Dilution Method In Bod
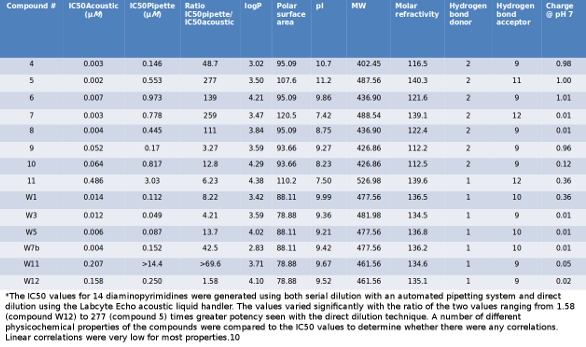
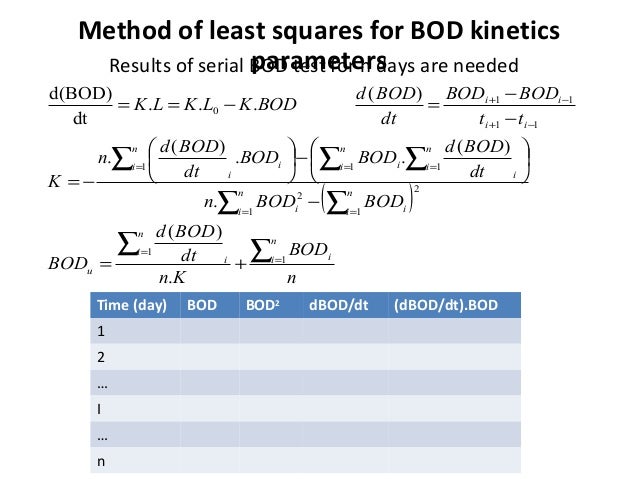
Understanding dilution and seeding procedures in BOD test New Delhi, May 1999 CSMRS Building, 4th Floor, Olof Palme Marg, Hauz Khas. Required for biochemical oxygen demand measurement. Modules in which prior training is. Measurement by Winkler method 5. Dec 25, 2013 Serial Dilution Method: Definition and Procedure Explained http://www.biologyexams4u.com/2013/12/serial-dilution-protocol-pdf.html.
This study aimed at monitoring the changes of fluorescent components in wastewater samples from 22 Korean biological wastewater treatment plants and exploring their prediction capabilities for total organic carbon (TOC), dissolved organic carbon (DOC), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), and the biodegradability of the wastewater using an optical sensing technique based on fluorescence excitation emission matrices and parallel factor analysis (EEM-PARAFAC). Three fluorescent components were identified from the samples by using EEM-PARAFAC, including protein-like (C1), fulvic-like (C2) and humic-like (C3) components. C1 showed the highest removal efficiencies for all the treatment types investigated here (69% ± 26%–81% ± 8%), followed by C2 (37% ± 27%–65% ± 35%), while humic-like component ( i.e., C3) tended to be accumulated during the biological treatment processes. The percentage of C1 in total fluorescence (%C1) decreased from 54% ± 8% in the influents to 28% ± 8% in the effluents, while those of C2 and C3 (%C2 and%C3) increased from 43% ± 6% to 62% ± 9% and from 3% ± 7% to 10% ± 8%, respectively. The concentrations of TOC, DOC, BOD, and COD were the most correlated with the fluorescence intensity ( F max) of C1 ( r = 0.790–0.817), as compared with the other two fluorescent components. The prediction capability of C1 for TOC, BOD, and COD were improved by using multiple regression based on F max of C1 and suspended solids (SS) ( r = 0.856–0.865), both of which can be easily monitored in situ.
The biodegradability of organic matter in BOD/COD were significantly correlated with each PARAFAC component and their combinations ( r = −0.598–0.613, p. 1. Introduction The lack of clean and fresh water is a great challenge for sustainable development worldwide, thus the re-use and/or recycling of industrial or municipal wastewater after treatment are important to satisfy the growing demand for water []. Organic matter present in wastewater poses a major challenge for efficient treatment, since it may cause low coagulation efficiency, disinfection byproduct formation, membrane fouling, oxidant demand, and biomass growth [–]. Therefore, it is necessary to develop effective monitoring techniques for organic matter concentrations during the treatment process.
To apply these ligatures, choose Discretionary Ligatures from the OpenType panel menu.  Sentences that have more words that can fit into one line of text automatically wrap into the next line. The type of text justification when wrapping occurs sometimes causes unnecessary spaces to appear in the line that are not aesthetically pleasing or linguistically correct.
Sentences that have more words that can fit into one line of text automatically wrap into the next line. The type of text justification when wrapping occurs sometimes causes unnecessary spaces to appear in the line that are not aesthetically pleasing or linguistically correct.
Furthermore, a rapid, sensitive and real-time monitoring tool can ensure the reliability of wastewater treatment performance [,]. How to make war games terrain pdf download online. The monitoring of organic matter in the effluents from wastewater treatment plants is also very useful to evaluate the influence of effluent discharge on the water quality, the biogeochemical processes and the ecosystem functions of the receiving water []. Bulk organic matter is a complex mixture encompassing a variety of organic compounds which have different susceptibilities to coagulation, adsorption, photo-degradation and biodegradation [,,]. Biodegradability is the most critical factor when evaluating the removal performances of many wastewater treatment plants primarily relying on biological processes [].
- суббота 19 января
- 3